Multiplayer
Spawning brushes in multiplayer
Runtime brushes need to be spawned on the server and every client in a multiplayer game.
There are two methods to achieve that:
1. By using Replication
Replication is a good choice for non-Persistent brushes that can be moved, scaled or destroyed. As soon as a brush is spawned on the server, replication will spawn it on all the clients. Later, as the brush is moved, scaled or destroyed, that change will also be replicated to clients.
Futhermore, clients that connect mid-game will receive replication for all the exisitng non-Peristent brushes and will be able to recreate the modified landscape in sync with other players.
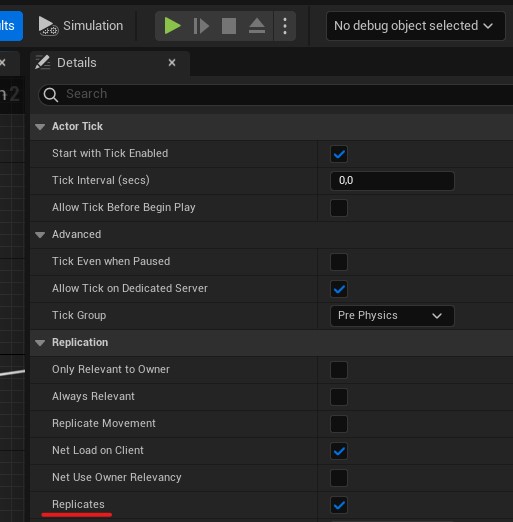
To enable replication for brushes ensure that Replicates property is set to true for the actors that contain the non-Persistent brush component.
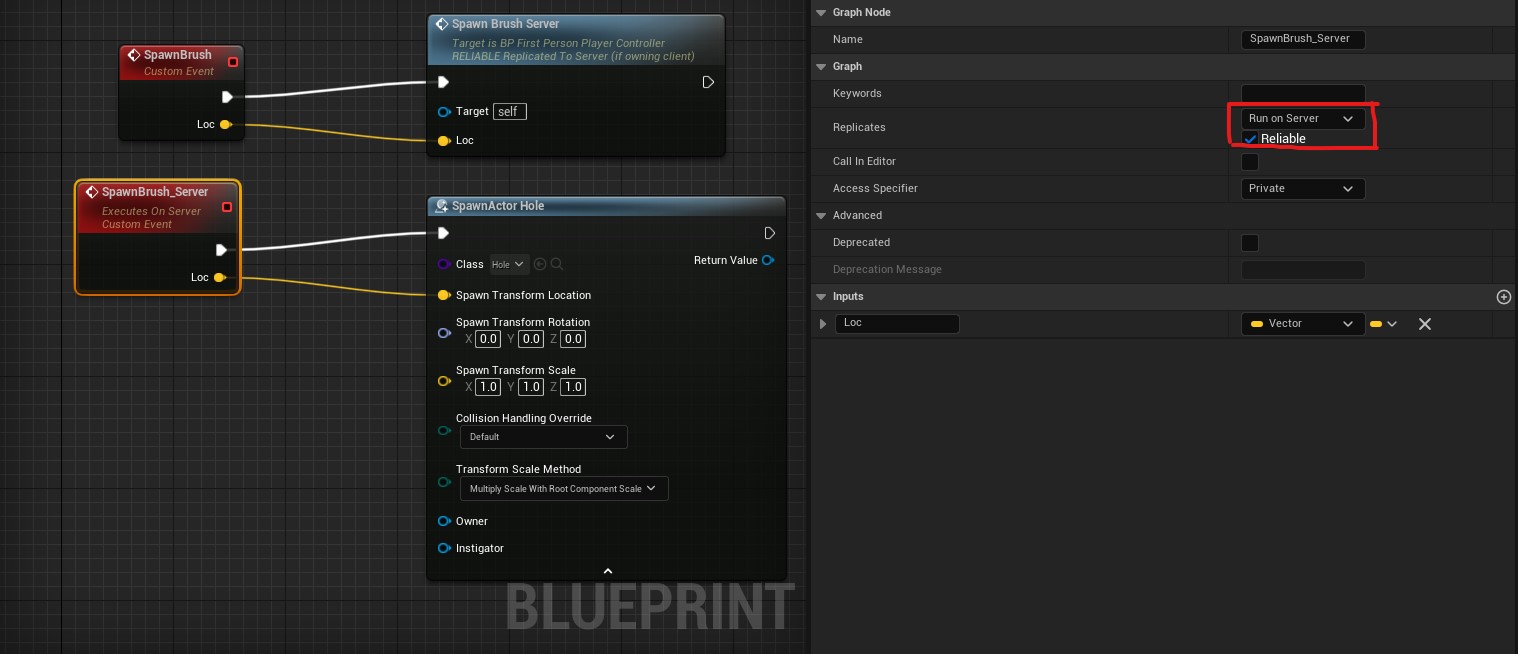
Spawning such a brush on the server will work out-of-the-box. To spawn a brush from a client, create an event that is run on the server reliably and call that event.
2. By using Multicast RPC
Replication doesn't work well for Persitent brushes, because they get destroyed as soon as they render (cache) into the Persistent Layer textures. As a result, replication might not have sufficient time to replicate this information to clients.
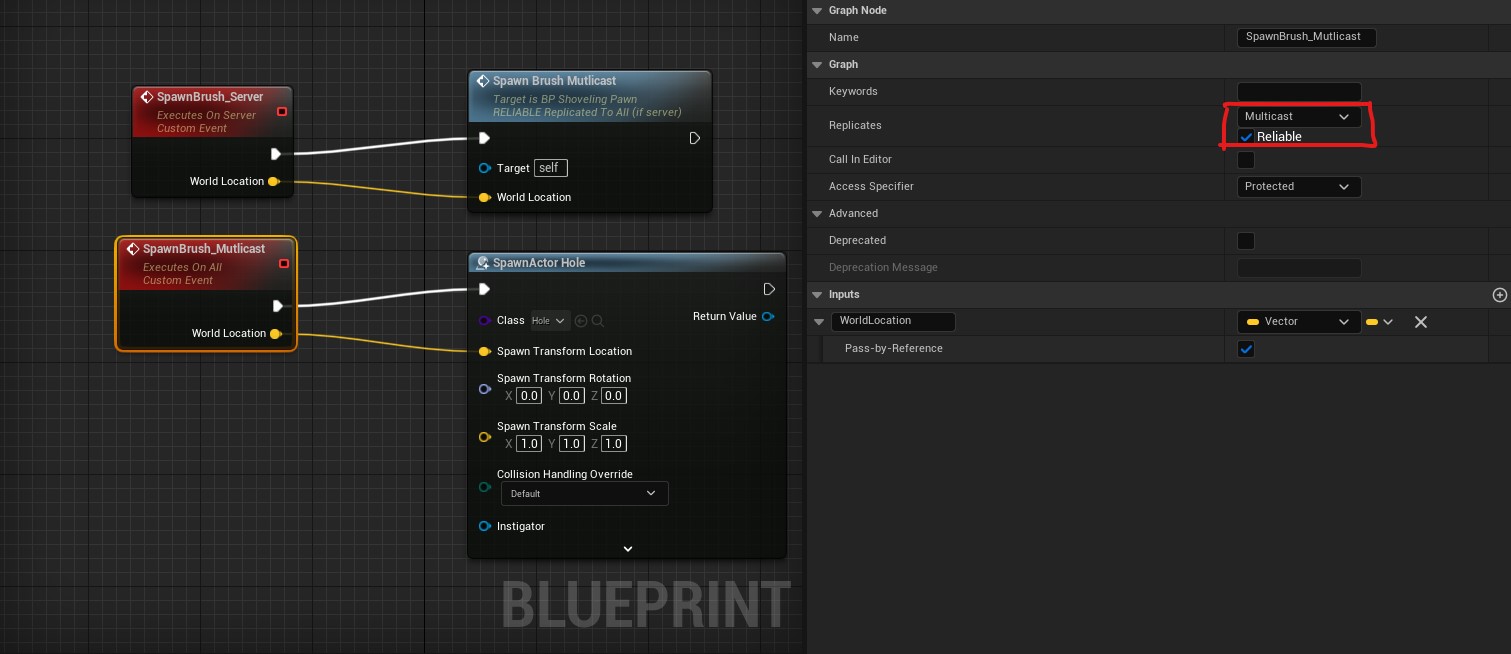
When using Multicast RPC, make sure the Replicates property is set to false for actors that contain Peristent brush components.
Spawn these brushes by calling the Multicast RPC from the server.
Joining mid-game
Players who join an ongoing game where landscape has already been modified by other players need to receive data about the landsape state, before they could start playing.
For non-Persistent brushes their data is sent with the initial replication. The only action that needs to be done is to trigger the landscape update once the replication data arrived. It can be done either by calling
UpdateLandscapefunction for each brush (probably in its OnRep/RepNotify function) or by callingUElRtWorldSubsystem::QueueRenderonce, after all the brushes replciated.For Persistent brushes, the results are cached into the Persistent Layer textures on the server. The new joining client needs to receive that cached data first. This process is performed by
ElRtDataTransfercomponent (Errant Landscape Runtime Persistent-Data Transfer Component). This component needs to be added to the PlayerController class. It will automatically detect a new player joining and will coordinate sending/receiving the Persistent Layer data.
Here is how the process of sending the Persistent data from the server (left) to a client (right) looks like.
Testing
One way to test joining mid-game is to first run the listen server and one or more clients, play the game for a bit and then run a command "open 127.0.0.1" on one of the clients. This will make the client reconnect to the local listen server mid-game. The same can be done in a packaged game.
To run a listen server in a packaged game, run "open MAPNAME?listen" command. So for example: "open ShovelingMap?listen".